Sales
What is the difference between the EasyOne Pro and Pro LAB?
The EasyOne Pro LAB is exactly the same as the EasyOne Pro, except that it has the capability to perform the multi-breath washout (MBW) test. This test requires additional sensors and the use of 100% Oxygen.
Where can I buy the annual replacement kit?
The annual replacement parts kit is available to purchase from your authorized ndd dealer or the ndd service department.
- North America - [email protected]
- International - [email protected]
What consumables are required for the EasyOne Pro/LAB?
Spirette: Each test performed requires the use of a spirette. This is a single-patient-use mouthpiece which ensures that no contamination can reach the internal flow path of the device. This means that no cleaning is required between patients, and no calibration, ever. Simply toss the spirette after each test session.
Barriette: For a DLCO test, in addition to the spirette, you will need to use a barriette. This protects the valve and hose system from contamination, eliminating the need for cleaning between patients.
FRC barriette: This is similar to the DLCO barriette, but used only when performing a multi-breath washout test.
Gasses: The DLCO test requires a standard medical grade DLCO gas mixture consisting of 0.3% Carbon Monoxide, 10% Helium, 21% Oxygen, remainder Nitrogen. The multi-breath washout test requires 100% Oxygen. These gasses are readily available from your local medical gas supplier in various tank sizes. We will assist you in selecting the appropriate tank regulators required for connection to the device.
How much space will an EasyOne Pro/LAB require in my office?
The device itself is self-contained and measures only 270 x 335 x 270 mm (10.6 x 13.2 x 10.6 inches) (h x w x d). No additional PC, monitor, keyboard or control unit is required. This allows it to easily fit on a counter. You will also need to allow for storage of the gas tank(s) which come in a variety of sizes, and can usually fit comfortably in a corner, or under the counter.
What are the maintenance requirements for the EasyOne Pro/LAB?
The EasyOne Pro/LAB is designed to require minimal maintenance. The annual replacement of four external components is ALL that is required to keep the system running smoothly. These components are available as a convenient kit. Installation is done in minutes and requires no special tools.
Is a laptop, PC or tablet provided with the system?
No, a laptop, PC or tablet must be purchased separately. The device specifications can be found in the Requirements PC/Laptop section under Specifications on the Easy on-PC page.
Where can I purchase the Easy on-PC?
All our products can be purchased through our authorized distribution partners. For US customers, please contact us to receive more information on finding your local dealer. International customers please click here for a list of dealers in your country.
Where can I purchase the EasyOne Air spirometer?
All our products can be purchased through our authorized distribution partners. Please contact us to receive more information on finding your local dealer.
What consumables are required for the EasyOne Air spirometer?
The EasyOne Air uses the patented ndd Flow Tube, a single-patient-use mouthpiece which ensures that no contamination can reach the internal flow path of the device. This means that no cleaning is required between patients, and no calibration, ever. Simply toss the Flow Tube after each test session.
What are the options and benefits of connecting the device to my PC?
EasyOne Connect is the free companion PC software for the EasyOne Air. It can be downloaded directly from our web site. Here are a few of the features and benefits of using EasyOne Connect:
- Long-term storage of test data
- Ability to enter patient demographics from the PC
- Connectivity with your EMR system
- Ability to over-read and manipulate data on the PC
- Export of data in many different formats, including the ability to create PDF reports
- Bluetooth allows wireless viewing of real-time curves on PC display, or use of real-time animated/pediatric incentives
- View and print trend graphs
- Create custom test report templates
How do you perform spirometry?
There are multiple steps for completing a spirometry test. For visual reference, you can review a video on how to perform a spirometry test by clicking the video button below.
- Take time to create a rapport with the patient—effective communication and participation between the patient and medical professional results in more consistent and robust testing results.
- Accurately measure the patient’s height.
- Carefully and correctly enter the patient data into the spirometer.
- Demonstrate the correct techniques and maneuvers to the patient prior to completing the test.
- Use body language to coach for a maximal inhalation.
- Loudly prompt them to BLAST out the air.
- For the next six seconds, quietly encourage the patient to continue BLASTING by saying, “keep going, keep going.”
- Monitor the patient carefully during the maneuvers.
- Obtain a good test session with a quality grade (A or B).
Meet Buddy—your spirometry coach, making spirometry testing easier and more enjoyable!
Learn more about Buddy!
How long does a spirometry test take?
A spirometry test typically takes 10 to 15 minutes, depending on the patient’s ability to follow instructions and complete the required breathing maneuvers. The test involves taking a deep breath and forcefully exhaling into a spirometry device multiple times to achieve accurate results.
Healthcare providers may repeat the test after administering a bronchodilator to assess lung function improvement. Proper coaching and technique are essential for reliable measurements.
Learn how to perform a spirometry test step by step.
Read the blog.
What are examples of obstructive lung diseases?
A few examples of obstructive lung disease include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Emphysema
- Chronic Bronchitis
- Asthma
- Bronchiectasis
What are examples of restrictive lung disease?
A restrictive lung disease is exactly that – one where a restriction occurs in the respiratory system.
A few examples of restrictive lung disease include:
- Interstitial lung diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Obesity
- Scoliosis
- Neuromuscular diseases such as muscular dystrophy or ALS
What are the disease states that are associated with high Diffusion Capacity (DLCO)?
- Asthma
- Left-to-right intracardiac shunts
- Polycythemia
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
Understanding lung function tests and their importance in respiratory health.
Read the blog
What are the disease states that are associated with low Diffusion Capacity (DLCO)?
- Emphysema
- Interstitial Lung Disease
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
- Chronic Pulmonary Emboli
- Anemia
- Left-sided heart disease (systolic and diastolic heart failure, Mitral Valve Disease)
Understanding lung function tests and their importance in respiratory health.
Read the blog
What are the important parameters in spirometry?
A spirometry test will produce a series of results or parameters that help medical professionals easily complete this exam. The three most important spirometry parameters are the FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC ratio parameters.
A simple guide to reading spirometry results.
Get the tips from Buddy
What indictations are used for spirometry?
There are multiple patient-symptoms or medical conditions that justify the use of spirometry. A few of the most common indicators include:
- To manage asthma and COPD patients
- Evaluate shortness of breath
- Perform surveillance for occupational-related lung disease
- Evaluate former or current smokers over the age of 45 for COPD
- Classification of COPD. (COPD is an umbrella term that covers multiple respiratory diseases including chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF))
- Monitor disease progression
- Measure response and progress due to treatment, medication, and respiratory therapy
- Smoking cessation
Tips from leading experts on the value of spirometry.
Watch the webinar
What is a complete pulmonary function test?
A complete pulmonary function test is a comprehensive assessment of lung function that includes three key components: spirometry (possibly pre/post bronchodilator), lung volume measurements, and diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO).
Together, these tests provide a full picture of how well the lungs are ventilating (moving air), how much air they can hold, and how efficiently they transfer gases like oxygen into the bloodstream.
Explore how ndd’s EasyOne solutions bring accuracy and ease to every step of pulmonary function testing.
Learn more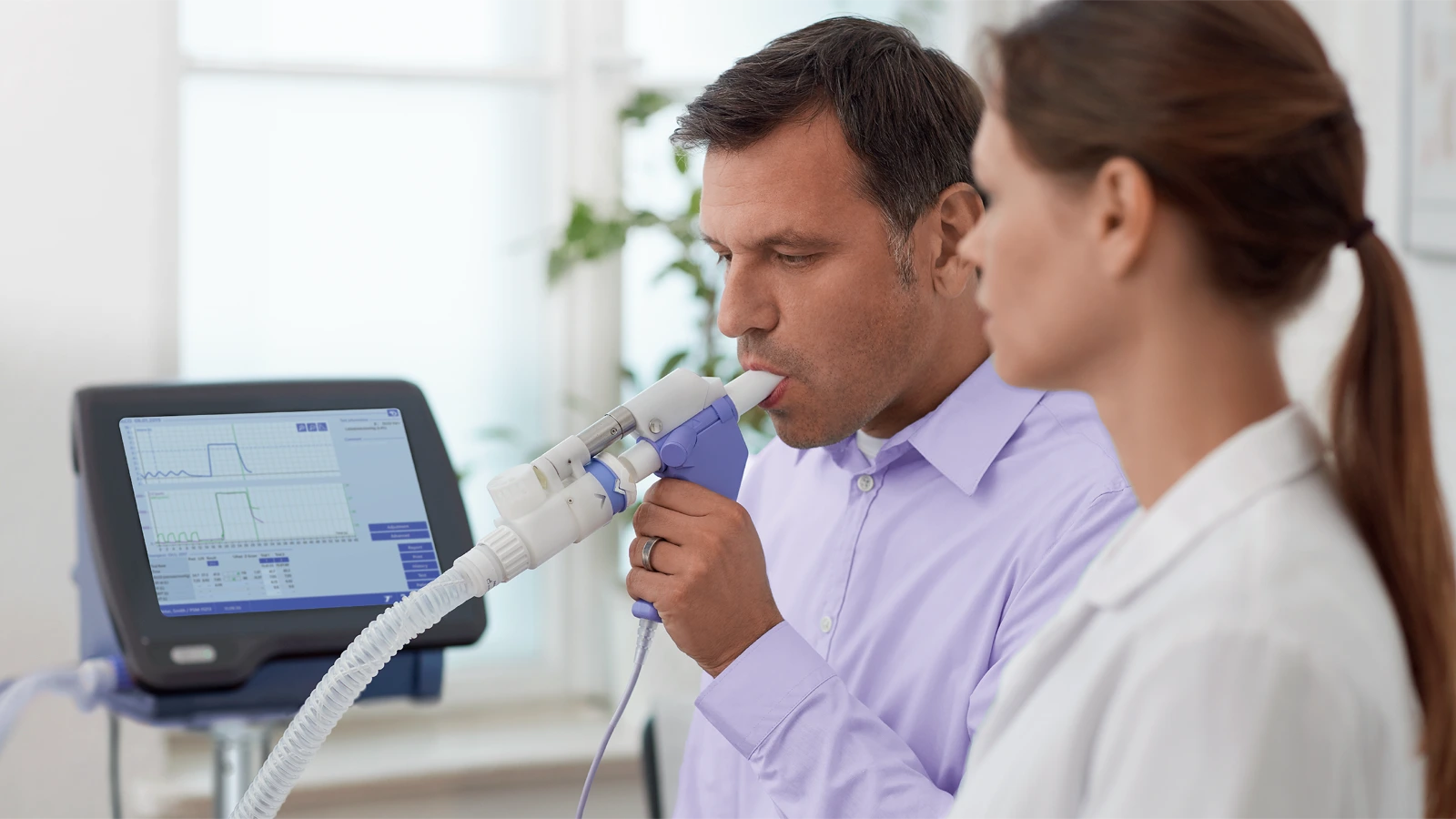
What is a diagnostic spirometer?
A diagnostic spirometer is a medical device that is used to measure lung function. It can be a portable or stationary spirometry device that is operated by a medical professional who is specially trained in proper testing procedures and techniques to produce a more consistent and reliable result.
ndd EasyOne spirometry solutions
Speak to a clinical specialist today!
###
What is a pulmonary function test?
A pulmonary function test (PFTs)are a group of noninvasive tests that monitor the performance of the lungs. They measure lung volume, capacity, rates of flow, and gas exchange.
Adding the following: PFTs typically include several different types of tests:
- Spirometry, which measures how much air you can breathe in and out and how quickly you can exhale.
- Lung volume measurement, which determines the total amount of air the lungs can hold.
- Diffusion capacity test (DLCO), which evaluates how efficiently gases like oxygen move from the lungs into the blood.
Together, these tests provide a comprehensive picture of lung function and can be used to monitor lung performance over time or assess the impact of environmental or occupational exposures.
EasyOne complete PFT and spirometry solutions
Discover the EasyOne solutions
What is Diffusion Capacity (DLCO) testing?
Diffusion capacity (DLCO) is a clinically useful test that provides a quantitative measure of gas transfer from the lungs to the blood. It complements spirometry in evaluating and managing patients with cardiac and/or respiratory disease.
Why DLCO is important in lung disease diagnosis and management:
- Helps differentiate between obstructive and restrictive lung patterns.
- Detects early changes in gas exchange, even when spirometry appears normal.
- Assists in evaluating interstitial lung diseases, such as pulmonary fibrosis.
- Useful for monitoring disease progression or response to treatment.
DLCO testing for COPD
Learn more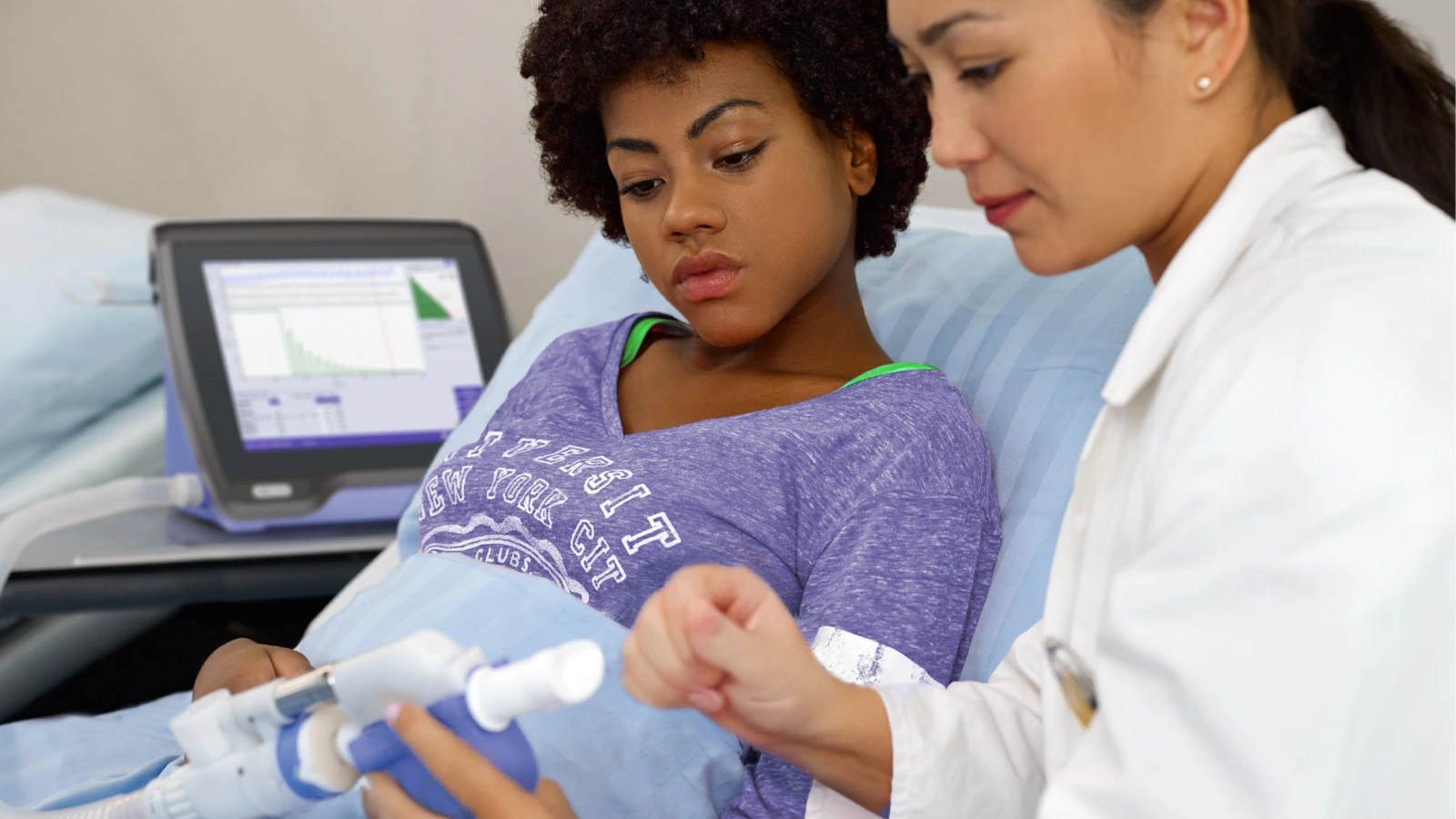
What is FEV1 in spirometry and what does it tell you?
FEV stands for Forced Expiratory Volume. The FEV1 parameter equates to the volume that is exhaled after one second. It is intended to measure the severity of an obstruction – with average FEV1 results measuring two to four liters. A lower FEV1 result equates to higher obstruction.
A simple guide to reading spirometry test results.
Get the tips from Buddy
What is FVC in spirometry and what does it tell you?
FVC stands for Forced Vital Capacity. FVC determines the total exhaled volume of air. FVC tells the spirometry tester how much air volume the patient can exhale. The FVC will fall when the patient can’t inhale deeply or can’t exhale completely. The average FVC result for an elderly man is about four liters (one gallon) of air. The intent of this parameter is to detect restriction.
A simple guide to reading spirometry test results.
Get the tips from Buddy.
What is spirometry used for?
Spirometry is used to diagnose and monitor lung diseases, assess pulmonary function, and support occupational health screenings. Spirometry helps healthcare providers to:
- Diagnose respiratory conditions like COPD and asthma
- Monitor disease progression and treatment effectiveness in patients with chronic lung conditions
- Evaluate lung function in workplace health programs, particularly for individuals exposed to dust, chemicals, or other respiratory hazards
By using a diagnostic spirometer, medical professionals can detect lung diseases early, track changes over time, and ensure workplace safety.
Ready to add spirometry testing to your practice?
Discover more now.
What is spirometry?
Spirometry is the primary method of assessing overall lung function. It works by measuring the volume of air that a patient can forcefully expel from the lungs after inhaling as much as possible. This non-invasive test is completed by medical professionals and is essential for diagnosing and monitoring respiratory conditions like COPD, asthma, and other lung diseases.
Using a diagnostic spirometer, a trained healthcare professional can assess lung health, detect early signs of disease, and guide treatment decisions.
Discover our advanced spirometry solutions here.
Book a demo today!
What is the difference between spirometry and a pulmonary function test (PFT)?
A spirometry test is a specific type of pulmonary function test. Spirometry measures the lungs volume (or how much) and flow (how quickly) the patient can move air into and out of their lungs. Spirometry will tell the tester if the patient has an obstruction, restriction, a mixed defect, or has normal lung flow.
Spirometry does NOT look at gas exchange and does not provide absolute lung volumes (RV, FRC, and TLC).
Diffusion capacity or transfer factor of the lung for carbon monoxide (CO) is known as a DLCO test. This measures the gas exchange and is used in conjunction with spirometry to provide a differential diagnosis. DLCO is also used to assess disease severity and is one of the best correlates of emphysema in COPD.
The final component that completes the full PFT exam is measuring absolute lung volume (RV, FRC, and TLC). This is completed by measuring body plethysmography, gas dilution, or nitrogen washout. Lung volumes are commonly used for the diagnosis of restriction. In obstructive lung disease, they are used to assess for hyperinflation. The changes in lung volumes can also be seen in a number of other clinical conditions.
Want to learn more about adding PFT and spirometry to your practice?
Get a live demo today!
What is the FEV1/FVC Ratio in spirometry and what does it tell you?
The FEV1/FVC ratio is typically expressed as a percentage (such as 75%). Nearly three-fourths of lung volume can normally be exhaled during the first second of the spirometry test. As such, the normal ratio falls between 65 to 85 percent. The range of normal FEV1/FVC ratio is determined by the patient’s age.
A simple guide to reading spirometry test results.
Get the tips from Buddy.
What will lung volumes show you?
Lung volumes are used to diagnose restrictive lung disease and to assess for hyperinflation in obstructive lung disease. With restrictive lung disease, TLC, VC, and RV may be decreased due to the inability of the lungs to expand properly.
The lungs are restricted from fully expanding and filling with air. In an obstructive disease such as COPD, patients may develop hyperinflation, which will result in a higher than normal TLC and RV. Conversely, IC will be decreased due to air trapping in the lungs.
Lung volume testing with the EasyOne Pro LAB provides fast, accurate, and fully automated measurements without the need for a body box. Its compact design and TrueFlow and TrueCheck technologies ensure reliable results for comprehensive lung assessment in most clinical settings.
EasyOne Pro LAB - Portable DLCO, MBW, Lung Volumes, LCI and Spirometry
Discover the benefits
When would you use DLCO testing?
Diffusion capacity testing (DLCO) is best used to pinpoint the type of respiratory disease. It is completed after spirometry when an obstruction or lung volume issues are predetermined.
- Differentiating emphysema from obstructive bronchitis and chronic asthma
- Assessment of COPD
- Detection of pulmonary vascular disease
- Assessment of shortness of breath (SOB)
- Disability/Impairment evaluations for ILD or COPD
